5 Draft Bill Facts

Understanding the Draft Bill: A Comprehensive Overview

The draft bill is a proposed legislation that outlines the framework for a new law. It is a crucial document that shapes the future of a country, state, or organization. In this article, we will delve into the world of draft bills, exploring their significance, key components, and the process of becoming a law.
What is a Draft Bill?
A draft bill is a document that contains the proposed text of a new law. It is prepared by a government agency, legislative committee, or interest group and is intended to be introduced into a legislative body for consideration. The draft bill serves as a starting point for discussion, debate, and negotiation among lawmakers.
Key Components of a Draft Bill
A typical draft bill consists of several key components, including: * Title and preamble: The title provides a brief summary of the bill, while the preamble explains the purpose and intent behind the legislation. * Definitions: This section defines key terms and phrases used throughout the bill. * Substantive provisions: These are the core sections of the bill that outline the proposed law, including any new rights, duties, or penalties. * Amendments and repeals: This section identifies any existing laws that will be amended or repealed by the proposed legislation. * Effective date and applicability: The draft bill specifies when the new law will come into effect and to whom it will apply.
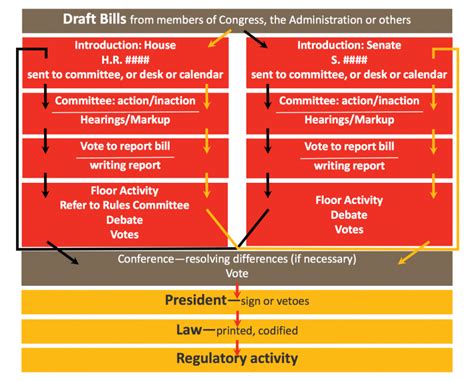
The Legislative Process: From Draft to Law

The journey of a draft bill to becoming a law is a complex and often lengthy process. Here are the general steps involved: * Introduction: The draft bill is introduced into the legislative body, usually by a member of the legislature or a government minister. * First reading: The bill is read for the first time, and lawmakers may debate its general principles. * Committee stage: The bill is referred to a committee, which examines the proposal in detail, hears evidence from experts and interest groups, and may propose amendments. * Report stage: The committee reports back to the legislative body, and lawmakers debate the bill and any proposed amendments. * Third reading: The bill is read for the third time, and lawmakers vote on its final passage. * Assent: If the bill passes, it is sent to the head of state (e.g., president or monarch) for signature or assent, which makes it a law.
Importance of Draft Bills

Draft bills play a vital role in shaping the legislative landscape. They: * Provide a framework for discussion: Draft bills serve as a starting point for debate and negotiation among lawmakers, interest groups, and the public. * Influence policy development: The proposed legislation can shape the direction of policy and have a significant impact on various sectors, such as economy, healthcare, or education. * Reflect societal values: Draft bills often reflect the values and priorities of a society, as they address issues that are relevant to the population.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Draft Bills

The process of creating and passing a draft bill can be contentious and challenging. Some common issues include: * Lobbying and special interest groups: Various groups may attempt to influence the legislative process to advance their own interests. * Partisan politics: Lawmakers may be divided along party lines, leading to conflicts and delays in the legislative process. * Constitutional concerns: Draft bills may raise constitutional questions or challenges, which can lead to court battles and delays.
💡 Note: The legislative process can be complex and time-consuming, and draft bills may undergo significant changes before becoming a law.
Best Practices for Engaging with Draft Bills

To effectively engage with draft bills, it is essential to: * Stay informed: Follow the legislative process and stay up-to-date on the latest developments. * Provide feedback: Share your thoughts and opinions on the proposed legislation with lawmakers and interest groups. * Participate in public consultations: Attend public hearings and consultations to provide input and shape the legislative process.
In the end, understanding draft bills and the legislative process is crucial for anyone interested in shaping the future of their country, state, or organization. By engaging with draft bills and providing feedback, individuals can contribute to the development of effective and meaningful laws that reflect the values and priorities of society.
What is the purpose of a draft bill?

+
The purpose of a draft bill is to propose a new law or amend an existing one, outlining the framework and key components of the legislation.
How does a draft bill become a law?

+
A draft bill becomes a law through a process of introduction, debate, committee review, and voting in the legislative body, followed by assent from the head of state.
Can anyone provide feedback on a draft bill?
+
Yes, anyone can provide feedback on a draft bill by sharing their thoughts and opinions with lawmakers, interest groups, or through public consultations.