10 National Guard MOS

Introduction to National Guard MOS

The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. It plays a crucial role in the country’s defense and security, with members serving both federal and state missions. One of the key aspects of a National Guard career is the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS), which represents the specific job or role that a soldier or airman is trained to perform. In this blog post, we will explore ten National Guard MOS options across both the Army and Air National Guard, highlighting the diversity of roles available to those who serve.
Army National Guard MOS

The Army National Guard offers a wide range of MOS options, catering to various skills and interests. Here are five examples:
- 11B - Infantryman: Infantrymen are the backbone of the Army, responsible for defending the country against any threat by land. They are trained to engage and destroy enemy forces, conduct reconnaissance, and gather intelligence.
- 13B - Cannon Crewmember: Cannon crewmembers are crucial in artillery units, responsible for loading and firing howitzers and other artillery pieces. They play a key role in supporting infantry and armor units on the battlefield.
- 15Q - Air Traffic Control Operator: Air traffic control operators are responsible for directing aircraft, managing air traffic patterns, and ensuring safe distances between aircraft. This MOS requires strong communication and organizational skills.
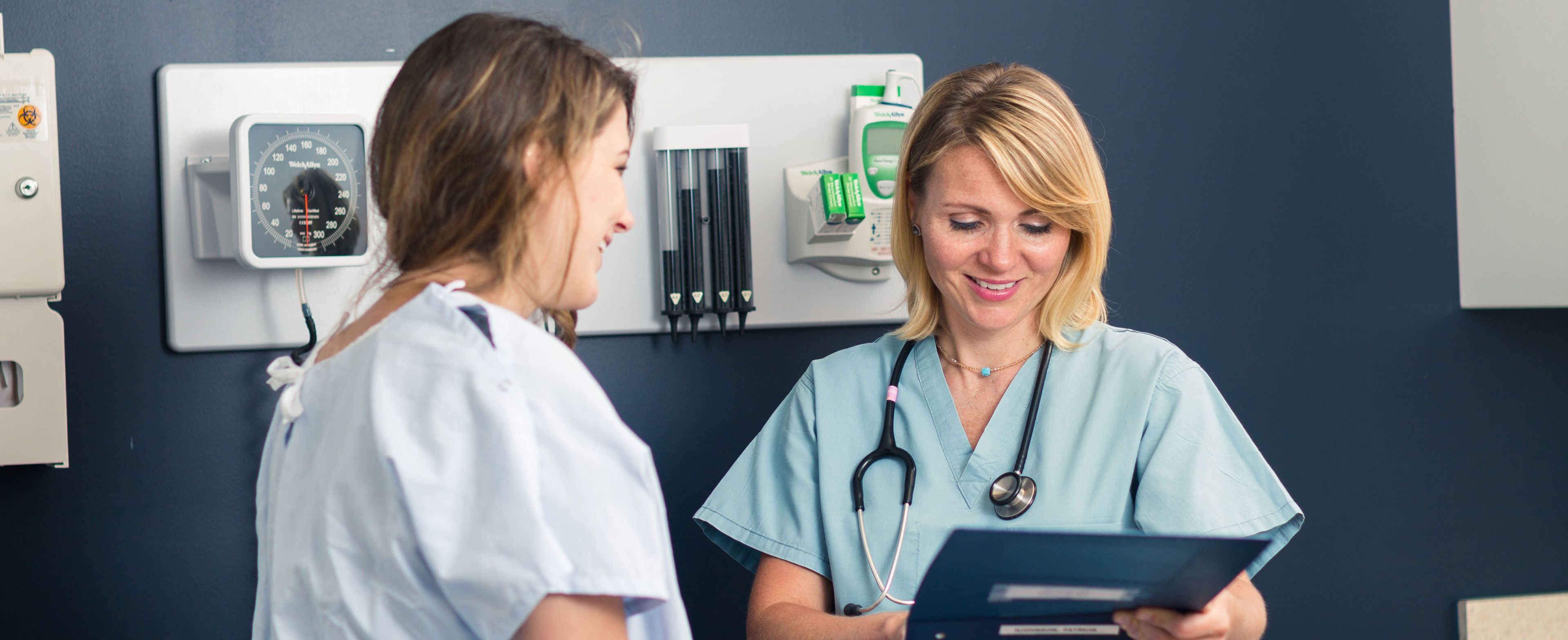
- 68W - Health Care Specialist: Health care specialists, also known as combat medics, provide medical care to soldiers in combat and non-combat situations. They are trained in basic life support, trauma care, and medical evacuation procedures.
- 88M - Transportation, General: Transportation specialists are responsible for operating and maintaining vehicles, managing transportation operations, and ensuring the safe movement of personnel and equipment.
Air National Guard MOS

The Air National Guard also offers a variety of career fields, including:
- Aircraft Maintenance: Air National Guard aircraft maintenance personnel are responsible for ensuring that aircraft are airworthy and ready to fly. This includes performing routine maintenance, repairs, and inspections.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity specialists in the Air National Guard work to protect computer systems and networks from cyber threats. They monitor network activity, identify vulnerabilities, and develop strategies to prevent cyber attacks.
- Intelligence: Intelligence analysts in the Air National Guard analyze data and information to provide critical support to military operations. They identify trends, patterns, and potential threats, helping commanders make informed decisions.
- Pilot: Pilots in the Air National Guard fly a variety of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters. They undergo extensive training to develop the skills needed to operate aircraft safely and effectively.
- Security Forces: Security forces personnel in the Air National Guard are responsible for maintaining base security, enforcing laws and regulations, and protecting personnel and resources.
Education and Training

Regardless of the MOS, National Guard members undergo comprehensive education and training to prepare them for their roles. This includes Basic Combat Training (BCT) for Army National Guard members and Basic Military Training (BMT) for Air National Guard members, followed by Advanced Individual Training (AIT) or technical school to learn the specific skills required for their MOS.
Career Opportunities and Benefits

Serving in the National Guard offers a range of career opportunities and benefits, including: - Education Benefits: The National Guard offers education benefits, such as the Montgomery GI Bill and tuition assistance, to help members pursue higher education. - Career Advancement: With experience and additional training, National Guard members can advance in rank and take on more senior roles within their MOS or transition into new career fields. - Leadership Opportunities: The National Guard provides opportunities for members to develop leadership skills, leading teams and making critical decisions. - Camaraderie and Esprit de Corps: National Guard service fosters strong bonds among members, creating a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps.
💡 Note: The specific benefits and opportunities available can vary depending on the state, MOS, and individual circumstances.
Conclusion and Future Outlook

In conclusion, the National Guard offers a diverse range of MOS options for those looking to serve their country, develop new skills, and pursue a meaningful career. Whether in the Army National Guard or the Air National Guard, members have the opportunity to contribute to national defense, respond to state emergencies, and grow both personally and professionally. As the world and the nature of conflict continue to evolve, the roles and missions of the National Guard will adapt, ensuring that its members remain critical to the nation’s security and well-being.
What is the difference between the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard?

+
The main difference lies in their mission and the types of operations they conduct. The Army National Guard focuses on land-based operations, while the Air National Guard is involved in air operations, including flying aircraft and managing air bases.
How do I choose the right MOS for me?

+
Choosing the right MOS involves considering your skills, interests, and career goals. It’s also important to research different MOS options and speak with recruiters or current National Guard members to get a better understanding of what each role entails.
Can I serve part-time in the National Guard and have a civilian career?
+
Yes, many National Guard members serve part-time, typically attending drills one weekend a month and completing a two-week annual training. This schedule allows them to pursue civilian careers and education while also serving their country.