Fighter Aircraft Size Comparison

Introduction to Fighter Aircraft

Fighter aircraft have been a crucial part of military forces around the world for decades. These aircraft are designed for air-to-air combat and are typically characterized by their high speed, maneuverability, and weaponry. Over the years, fighter aircraft have evolved significantly, with advancements in technology leading to improvements in their design, capabilities, and size. In this article, we will delve into the world of fighter aircraft, exploring their history, development, and size comparison.
History of Fighter Aircraft
The first fighter aircraft were developed during World War I, with the primary goal of shooting down enemy aircraft. These early fighter planes were simple, lightweight, and armed with machine guns. As technology advanced, so did the design and capabilities of fighter aircraft. During World War II, fighter aircraft played a significant role in the war, with the introduction of more powerful engines, radar technology, and advanced weaponry. The post-war period saw the development of jet-powered fighter aircraft, which further increased their speed and maneuverability.
Development of Modern Fighter Aircraft

Modern fighter aircraft are highly advanced machines, with sophisticated designs, materials, and technologies. They are typically made of lightweight materials, such as carbon fiber and titanium, which provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Advanced avionics, including radar, electronic warfare systems, and communication systems, enable pilots to detect and engage enemy aircraft from long distances. Additionally, modern fighter aircraft are equipped with a range of weaponry, including missiles, rockets, and guns.
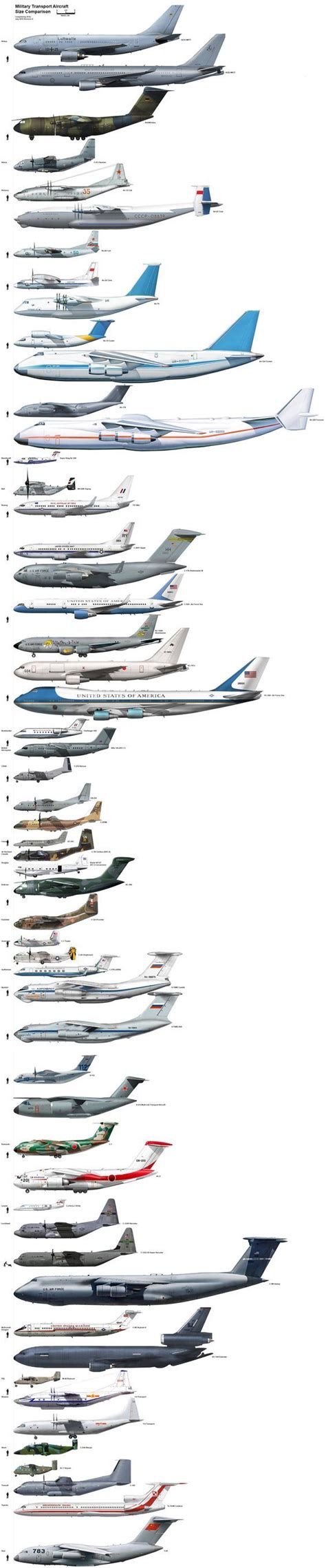
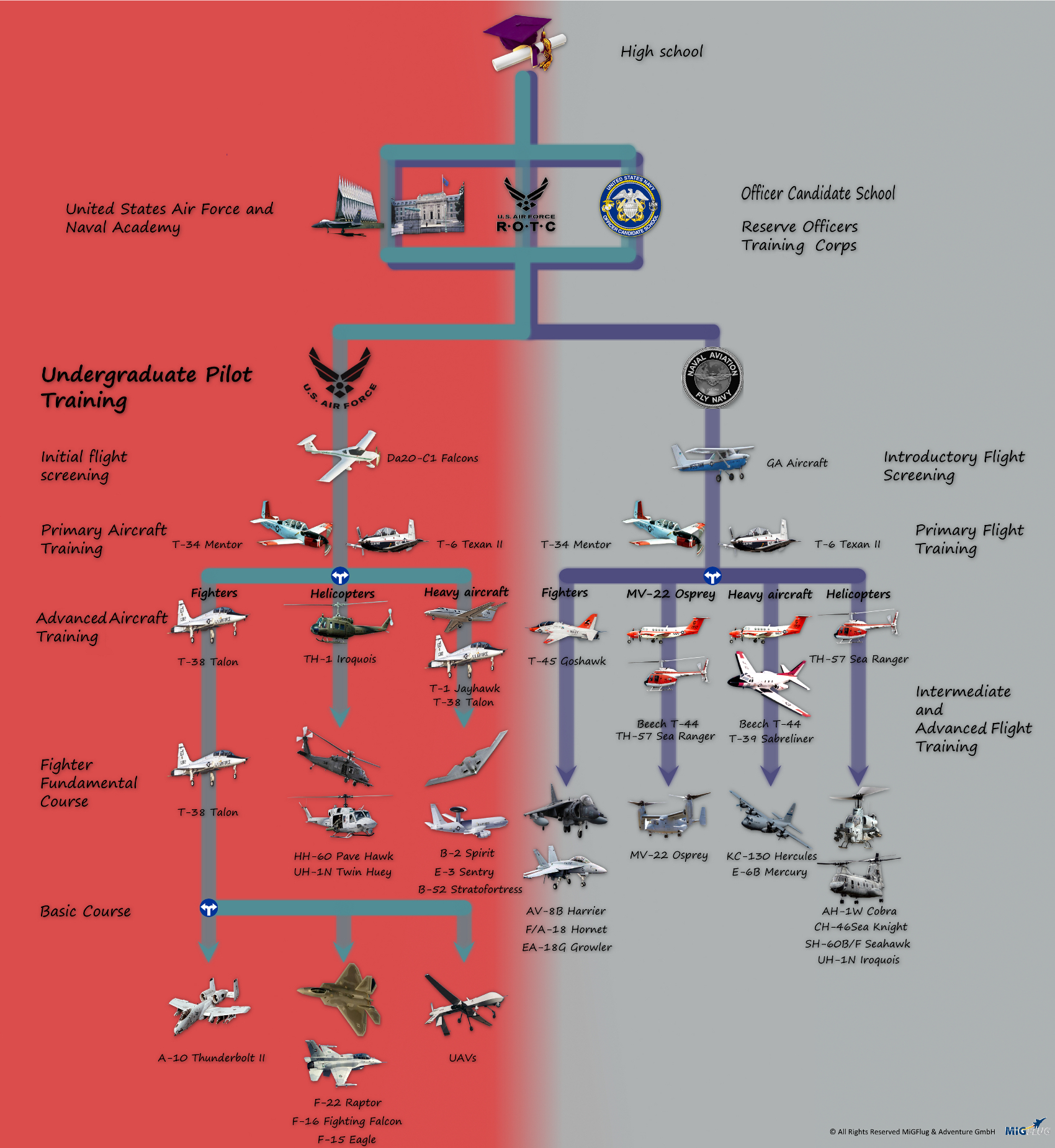
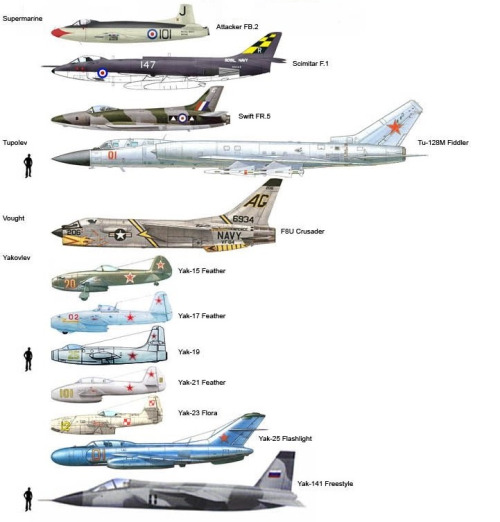
Size Comparison of Fighter Aircraft

The size of fighter aircraft can vary significantly, depending on their design, role, and generation. Here is a comparison of some of the most notable fighter aircraft:
- F-16 Fighting Falcon: length 49.4 ft (15.1 m), wingspan 32.8 ft (10 m), height 16.7 ft (5.1 m)
- F-15 Eagle: length 63.8 ft (19.4 m), wingspan 42.8 ft (13 m), height 18.5 ft (5.6 m)
- F-22 Raptor: length 62.1 ft (18.9 m), wingspan 44.6 ft (13.6 m), height 17.8 ft (5.4 m)
- F-35 Lightning II: length 50.5 ft (15.4 m), wingspan 35 ft (10.7 m), height 14.2 ft (4.3 m)
- MiG-25 Foxbat: length 73.9 ft (22.5 m), wingspan 47.8 ft (14.6 m), height 20.7 ft (6.3 m)
- SAAB Gripen: length 46.3 ft (14.1 m), wingspan 30.8 ft (9.4 m), height 14.9 ft (4.5 m)
| Aircraft | Length (ft) | Wingspan (ft) | Height (ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F-16 Fighting Falcon | 49.4 | 32.8 | 16.7 |
| F-15 Eagle | 63.8 | 42.8 | 18.5 |
| F-22 Raptor | 62.1 | 44.6 | 17.8 |
| F-35 Lightning II | 50.5 | 35 | 14.2 |
| MiG-25 Foxbat | 73.9 | 47.8 | 20.7 |
| SAAB Gripen | 46.3 | 30.8 | 14.9 |

Key Factors Affecting Fighter Aircraft Size

Several factors influence the size of fighter aircraft, including:
- Role: The primary role of the aircraft, such as air-to-air combat, air-to-ground strikes, or reconnaissance, affects its size and design.
- Technology: Advances in technology, such as materials, avionics, and engines, enable the development of smaller, more efficient aircraft.
- Speed and maneuverability: The need for high speed and maneuverability can result in larger aircraft, as more powerful engines and larger control surfaces are required.
- Stealth capabilities: The incorporation of stealth technology, which reduces an aircraft’s radar cross-section, can lead to unique designs and sizes.
🚀 Note: The size of fighter aircraft can also be influenced by the availability of resources, such as funding and production capacity.
In summary, the size of fighter aircraft is a critical factor in their design and development. By understanding the history, development, and key factors affecting fighter aircraft size, we can appreciate the complexity and sophistication of these machines.
The main points to take away from this article are the importance of considering the role, technology, speed, and stealth capabilities when designing fighter aircraft, as well as the impact of these factors on their size. Additionally, the size comparison of various fighter aircraft provides a useful reference for understanding the differences between these machines.
To further illustrate the points made in this article, consider the following key takeaways: * Fighter aircraft have evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology leading to improvements in their design, capabilities, and size. * The size of fighter aircraft can vary significantly, depending on their design, role, and generation. * Key factors affecting fighter aircraft size include role, technology, speed, and stealth capabilities. * The incorporation of stealth technology can lead to unique designs and sizes.
What is the primary role of fighter aircraft?
+
The primary role of fighter aircraft is air-to-air combat, although they can also be used for air-to-ground strikes and reconnaissance.
What factors influence the size of fighter aircraft?

+
Key factors affecting fighter aircraft size include role, technology, speed, and stealth capabilities.
How has the development of stealth technology impacted fighter aircraft design?

+
The incorporation of stealth technology has led to unique designs and sizes, as it reduces an aircraft’s radar cross-section, making it more difficult to detect.



